
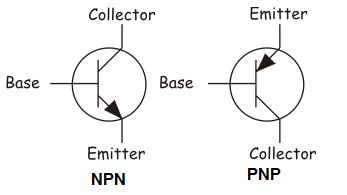
Finally, the Body of the device isn't relevant to processor so we won't discuss it here. The Gate is the switch used to turn the transistor on and off. In an n-channel device it typically goes in the drain and out the source while in an p-channel device, it typically flows in the source and out the drain.
The current we are controlling flows through the Source and Drain. The transistors used in integrated circuits, known as MOSFETs (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors), have four connections. Now that we can control the electrical conductivity of certain parts of our silicon, we can combine the properties of multiple regions to create transistors. The specific processes to add these impurities to the silicon are known as Ion Implantation and Diffusion and they are bit beyond the scope of this article. This is where the "p" in p-type and pMOS come from. By adding electron acceptor elements like boron, indium, or gallium to the silicon, we can create a p-type region which is positively charged. This is where the name n-type and the "n" in nMOS comes from. Since the silicon area where these elements were applied now has an excess of electrons, it will become negatively charged. If we add a precisely controlled amount of electron donor elements like arsenic, antimony, or phosphorus, we can create an n-type region. The fabrication process of a wafer before the chips are packaged. Just like there are two types of transistors, there are two main corresponding types of doping. The goal here is to change the way electrons behave so that we can control them. The doping process involves adding carefully selected impurities to the base silicon substrate to change its conductivity.

To turn a wafer of silicon into a useful circuit by adding transistors, fabrication engineers use a process called doping. Silicon is known as a semiconductor because it doesn't fully conduct or insulate it's somewhere in the middle. The base structure of a processor that the transistors are built into is silicon. We discussed how there are two main types of transistors: nMOS devices which allow current when the gate is on, and pMOS devices which allow current when the gate is off. A transistor is an electronically controlled switch that we can turn on or off by applying or removing voltage from the gate. (Sea of Accelerators, 3D integration, FPGAs, Near Memory Computing)Īs we discussed before, processors and all other digital logic are made out of transistors. Part 4: Current Trends and Future Hot Topics in Computer Architecture
Part 3: Laying Out and Physically Building the Chip (schematics, transistors, logic gates, clocking) (instruction set architectures, caching, pipelines, hyperthreading) Part 1: Computer Architecture Fundamentals


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
